What Is Financial Consolidation? Process & Best Practices
- andrewmichaelfriedrichs
- November 1, 2022
- Bookkeeping
- 0 Comments

However, if the parent company is the primary beneficiary of the VIE, consolidation is required to reflect the economic realities of the parent’s involvement. New technology like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) will be able to handle more complex manual tasks in financial consolidation. AI-driven predictive analytics will help identify patterns in financial data, which can improve forecasting and business planning. Highradius stands out in the financial consolidation space by delivering practical, results-driven AI for record to report processes. Our platform has over 200 LiveCube agents that automate more than 60% of close tasks.
- In a divestiture scenario, one company sells off all or part of its assets to focus on core operations.
- This approach eliminates the complexities and potential distortions that might arise from intercompany transactions and balances.
- Consolidation can refer to using a single loan to pay off multiple consumer debts.
- Consolidation broadly refers to combining multiple entities into a larger one, whether financial accounts or corporations.
- It also helps give investors an accurate picture of the company’s overall performance and stability.
- It allows companies to quickly identify discrepancies between different sets of books or documents and ensure the numbers are accurate before presenting a final report.
Financial Consolidation: A Comprehensive Overview
- (3) The total capital profits—up to 1st June—are 1/4 of Rs 1,62.000 or Rs 40,500, i.e., 1/4 (2,88,000-1,12,000 – 14,000).
- Some banks will streamline this process with innovative tools for a hassle-free account switch complete in minutes.
- Quickonomics provides free access to education on economic topics to everyone around the world.
- Likewise, in scenarios where the investor controls less than 20% of shares and is significant, one uses equity consolidation.
- In this blog post, we delve into the concept of consolidation in accounting, explore the consolidation method and process, and discuss the rules that govern this practice.
- Parent companies need complete tax information from subsidiaries to prepare consolidated tax returns.
To ensure accuracy across all entities or subsidiaries, finance teams rely on both direct and indirect rates. It automates data collection, performing complex calculations and producing accurate reports automatically. Companies with multiple entities, subsidiaries, or complex structures find consolidated financials valuable in many ways. This complexity underscores the importance of having skilled professionals and robust systems in place to manage the consolidation process efficiently.
What Is the Impact of Consolidation in Accounting?
- The company may also decrease interest expense on retired debt or lose interest income on any balance sheet cash used to finance the deal.
- The effects of this consolidation are reflected in the parent’s overall financial position.
- These transactions must be analyzed and eliminated to avoid distortions in the consolidated financial data.
- Yes, minority interests (or non-controlling interests) are represented in consolidated accounts.
- Positive performance in other areas within the consolidated group may neutralize any negative impact on one company.
- This process takes a lot of time because it needs careful attention to detail and constant checking for mistakes or differences that could affect the end product’s accuracy.
Following this combination, a series of elimination and adjustment entries are made in the worksheet’s designated columns. A parent-subsidiary relationship forms when one company, the parent, gains control over another, the subsidiary. The determination of whether to consolidate financial statements hinges on this concept of control. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), a controlling financial interest is the factor that mandates consolidation. The consolidated statement of cash flows tracks cash inflows and outflows for both the parent company and its subsidiaries. Goodwill is treated as an intangible asset in the consolidated statement of financial position.
Consolidated Financial Statements: Requirements and Examples
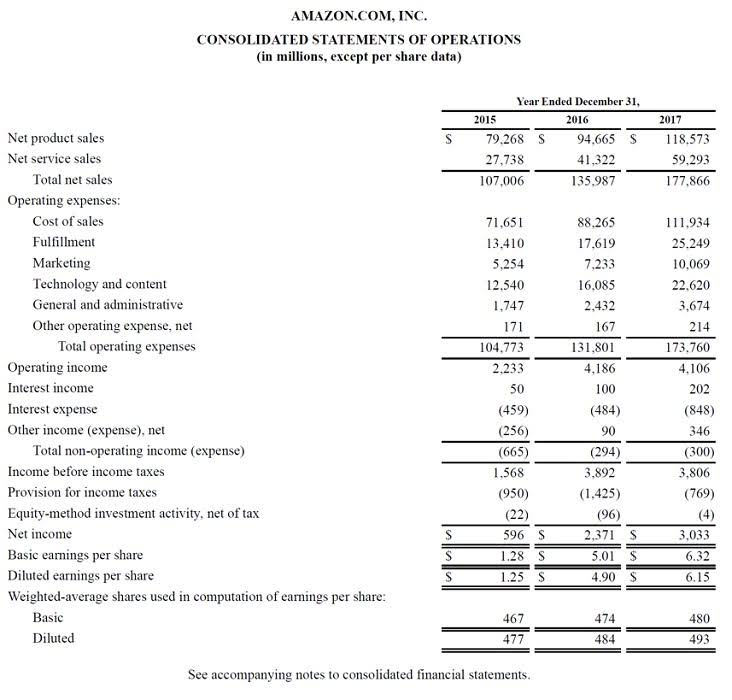
Private companies usually decide to include their subsidiaries on an annual basis. This annual decision is usually influenced by the tax advantages a company may obtain from filing a consolidated statement compared to filing an unconsolidated statement for a tax year. Public companies usually choose to create consolidated or unconsolidated financial statements for a longer period. Noncontrolling interests, or minority interests, represent the equity stake in a subsidiary not owned by the parent company. These are presented separately within the equity section of the consolidated balance sheet, highlighting the dual ownership structure.

Consolidation adds together the assets, liabilities and results of the parent and all of its subsidiaries. The investment in each subsidiary is replaced by the actual assets Mental Health Billing and liabilities of that subsidiary. The frequency of consolidation accounting depends on factors such as changes in ownership structure, regulatory requirements, and reporting obligations. Still, it may also be necessary when significant events, such as mergers or acquisitions, occur during the year.
- This makes sense if the interest burden of the new loan is lower than that of the two separate loans.
- The consolidated financial statements can also be presented to clients when it comes to concluding a major contract.
- In addition to this, realistic deadlines need to be set and reporting schedules should be aligned across entities.
- The decision of the former depends on the tax advantages they may reap from having a consolidated or unconsolidated financial statements.
- Consolidation accounting allows companies to centralize financial reporting and streamline the reporting process.
- Records should include invoices, bank statements, purchase orders and other relevant documents related to each transaction (such as receipts or contracts).
- To ensure consolidated financial statements reflect only realized profits, the unrealized profit is eliminated.
An example of investment consolidation used in accounting is a situation in which an investor has multiple investments across different asset classes and diverse risk profiles. The term first appeared in the early 1700s, when businesses began to merge and create larger, more vital entities. In the 1920s and 1930s, more and more companies joined, leading to an increased need for formal consolidation procedures. Third, consolidation does not necessarily mean that the newly created entity will have one single owner. There is nothing wrong with having a group of investors or owners come together to create a larger company. Three very important concepts in group accounting are goodwill, internal transactions https://foreward.my/overtime-calculator-to-calculate-time-and-a-half and non-controlling interest.

Who Needs Consolidated Financial Statements and Why

Consolidation also applies to debt repayment plans where individuals combine multiple debts into a single loan with lower interest rates to manage their finances better. The consolidation process requires careful attention to minority interests and the appropriate treatment of non-controlling interests. This adds a layer of complexity in determining the correct allocation of profits and losses. consolidated account meaning Adopting clear guidelines and consistent methodologies for handling these interests can help maintain accuracy and transparency in financial reporting.